
Pakistan’s Rising Health Crisis Fuelled by Antibiotic Misuse
Antibiotics are discovered to save lives; however, nowadays, their overuse or misuse in Pakistan is causing serious public health problems. People use antibiotics without any need or without a doctor’s prescription, which causes drug-resistant infection, more deaths and greater pressure on healthcare centres. This article examines the current trend of antibiotic use in Pakistan, the threat of antimicrobial resistance (AMR), and the actions needed to prevent a health crisis.
What Is Antibiotic Misuse And Its Effect
Antibiotic misuse refers to taking antibiotics for a viral infection when they are not necessary, or using the wrong ones, or stopping treatment too soon. This practice allows bacteria to survive in your body and become stronger, leading to antimicrobial resistance (AMR). AMR makes infection harder and even impossible to treat.
The World Health Organisation (WHO) report that many bacterial infections no longer respond to antibiotics, especially in a region of South Asia, due to the misuse of antibiotics. It’s become a serious global health threat.
Antibiotic Overuse In Pakistan

The conception of antibiotics in Pakistan has increased in recent years. According to industry data, conception reached 134.5 billion in 2022 and 17% rise from last year. Rs 126 billion was spent on antibiotics in 2024. The number shows that more people are using these medicines.
The increase in the use of antibiotics is due to easy access to them without a doctor’s prescription. Many pharmacies sell these antibiotics, which leads to self-medication.
Common reasons for the misuse of antibiotics in Pakistan are
- Easy access to antibiotics without a doctor’s prescription.
- Sometimes antibiotics are prescribed wrong, even for flu or a cold.
- People often stop taking their medication once they feel better.
- People in Pakistan have low knowledge about antimicrobial resistance and how to use antibiotics correctly.
The silent health threat
Pakistan faces many serious problems, as common infections are becoming harder and impossible to treat because antibiotics are not working on bacteria.
The challenge of drug-resistant typhoid
Typhoid fever, caused by Salmonella typhoid, is a bacterium that spreads through food or water, causing high fever, headache, abdominal pain and fatigue, leading to severe illness or death.
In typhoid patients, 1 out of 3 cases do not respond to antibiotics and, in some cases, to almost all medications. Studying Lahore found that a higher resistance of 56% of typhoid resistance was extensively drug resistant (XDR) and almost 22% world multidrug resistant (MDR). This thing leaves very few treatment options. In many cities, like Lahore and Karachi, people need expensive treatment because standard medications are not working for them.
Other infections
This problem is not only seen in typhoid. Bacteria in the mouth and other parts of the body also become resistant to common antibiotics like tetracycline and penicillin. Especially in people who have used antibiotics recently or regularly.
However, overuse of antibiotics leads bacteria to become stronger and makes everyday infections more expensive to treat in Pakistan.
Effect on health and economy
Antibiotic resistance is not only a problem in the medical field; it also affects our whole society.
Death rate
In Pakistan, around 200,00 to 300,000 people die each year due to drug-resistant infections.
Long illness, high cost
When an infection resists antibiotics, the patient has to stay longer in the hospital and use stronger medicines, which are expensive.
Hospitals under stress
Hospitals and ICUs are overstressed due to infections that are not responding to normal antibiotics.
Economic loss
When people become sick for a longer period, and they have to adopt an expensive treatment, it affects their work productivity and financial pressure increases on families and even on the country.
Causes of antibiotic misuse
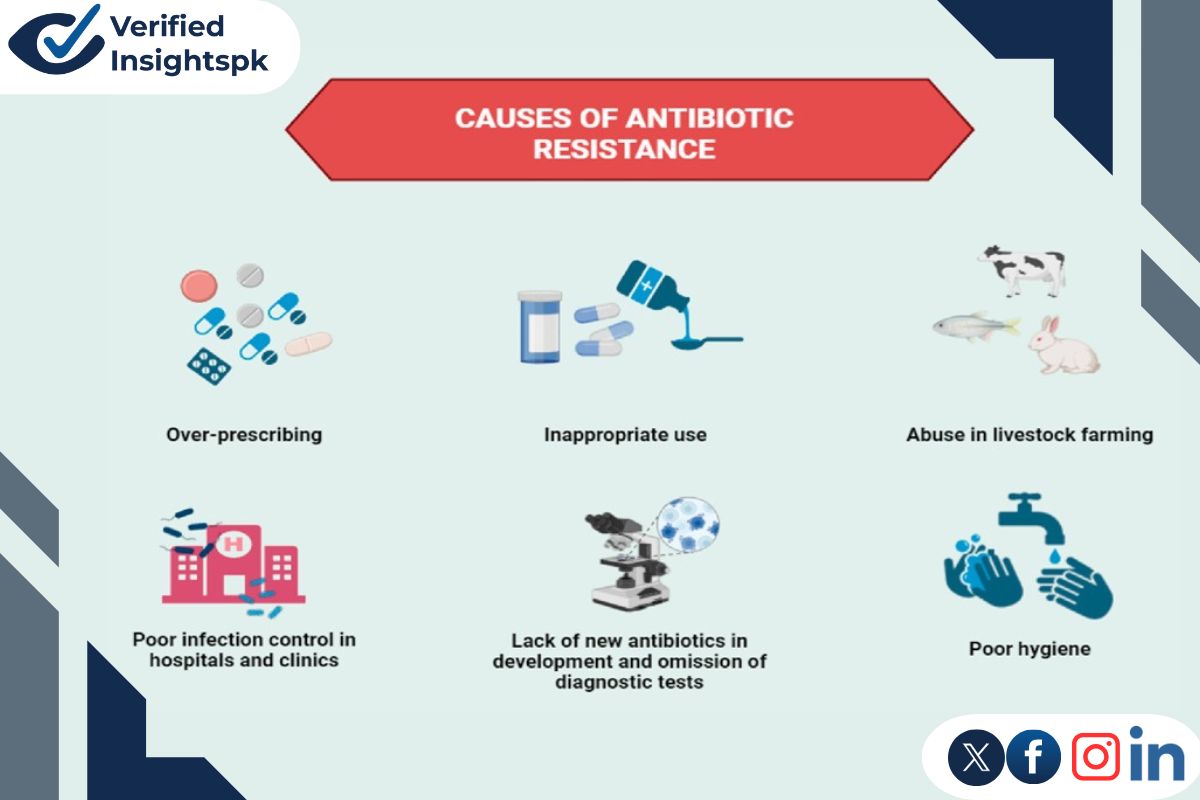
Several factors cause the misuse of antibiotics in Pakistan. Some of these are:
Easy to assess
About every pharmacy in Pakistan sells antibiotics without a doctor’s prescription.
Lack of tests
In Pakistan, especially in rural areas, many clinics cannot test properly to check which bacteria are causing infection. And doctors give antibiotics without finding out the real reason.
Low awareness
Many people are not well-educated to know when to use antibiotics. They think that antibiotics can cure all diseases. Even in cities, these wrong beliefs are common.
In animals
Many people use antibiotics in animals like cows and chickens to help them grow, which causes many bacteria that spread in humans.
Steps to control Antibiotic misuse
- Rules should be enforced so that antibiotics cannot be bought from pharmacies without a doctor’s prescription.
- Hospitals should use antibiotics correctly only when they are needed.
- Affordable tests should be provided so that doctors know which antibiotic will work for a person.
- Public awareness should be raised in order to tell people about the danger of the misuse of antibiotics and the importance of finishing the medicine course.
- Make policies and track them, and follow WHO guidelines.
Conclusion
A serious problem caused by antibiotic misuse in Pakistan is a growing health crisis that affects health, money, and society as a whole. Drug resistance and other bacteria make common infections harder and impossible to treat. Some steps, like making rules, educating people, and improving hospital practices, are needed to protect people from the misuse of these medicines.
Reference & Sources
World Health Organization (WHO) – Antimicrobial Resistance
NHS (National Health Service, UK) – Antibiotics Usage and Resistance
Disclaimer
The information provided in this article is intended for educational and informational purposes only. It does not constitute medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Antibiotic use, resistance, and related health conditions vary from person to person and should be addressed by qualified healthcare professionals.
Readers should consult a licensed medical practitioner, physician, or infectious disease specialist before making any decisions about antibiotic use, treatment plans, or health concerns related to drug resistance. The content in this article is based on general public health information and widely accepted guidelines, but individual health needs and responses may vary.
Verified Insights PK does not claim to provide medical or clinical advice. This article should not be used as a substitute for professional medical consultation, diagnosis, or treatment. Always rely on a trusted healthcare provider for personalized guidance.










